Mac Terminal Commands List. There are tons of commands that you can make use of. Let’s focus on some of the most common MacOS Terminal commands you need to be familiar with when you are mastering the Terminal. There are a few features that are applicable for any command. Mac Terminal Commands – Complete List This is a complete A- Z index of all Mac commands and the terminal events associated with those commands. We have compiled this list by using official sources and have explained more clearly and elaborately about each of them.
If you’re working in Terminal on your Mac, you need to know the most important UNIX commands: those that work with directories, those that work with files, and miscellaneous but commonly used commands.
Folders are called directories in UNIX. Commands that refer to filenames, as most do, assume that you’re talking about files in the working directory. When you open the Terminal window, the working directory is set to your home directory, abbreviated ~. Bash shows you the current working directory and your username to the left of its prompt. The following table lists common directory-related commands.
| Command | What It Does |
|---|---|
| ls | Lists the names of the files in the working directory. For more complete information, use ls –alF (. |
| cd directoryname | Changes the working directory to the one you named. |
| cd .. | Brings you up one directory level. |
| cd | Returns you to your home directory. |
| pwd | Displays the pathname of the current directory. |
| mkdir newdirectoryname | Makes a new directory. |
| rmdir directoryname | Removes (deletes) an empty directory. |
As in Windows, you can redirect the output of a command to a text file. So if you want a record of the files in a folder, type cd, followed by a space, drag the folder’s icon to the Terminal window, and press Return. Type ls > mydirectorylist.txt and press Return again. A file named mydirectorylist.txt will appear in the folder you chose. You can open the file in TextEdit to see a list of the files in that directory.
This table lists commands commonly used when working with files in the Terminal window.
| Command | What It Does |
|---|---|
| cp filename1 filename2 | Copies a file. |
| chmod | Changes permissions for access to a file. Study the man page before using this one. |
| diff | Compares two files line by line (assumes text). |
| more filename | Displays a text file one page at a time. Press the spacebar to see the next page; press Q to quit. The man command works through more. |
| mv filename1 filename2 | Moves a file or changes its name. |
| rm filename | Removes (deletes) a file. |
This last table explains other handy commands that anyone getting started in Terminal will likely want to know.
| Command | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Control+C | Terminates most operations. |
| date | Displays the current date and time. |
| echo | Repeats whatever appears after the command (after expansion). |
| help | Displays a partial list of bash commands. |
| history | Displays the last commands you typed. You can redo a command by typing an exclamation point (!) followed immediately (no space) by the number of that command in the history list. To repeat the last command, type !!. To repeat the last filename, type !*. |
| pico | A simple UNIX text editor. |
| ps | Displays a list of running processes. |
| sudo | Lets you carry out commands for which the account you are using lacks authority. You will be asked for an administrator’s password. |
When you’re working in Terminal, you don’t have a Trash Can to which deleted files are moved pending ultimate disposal. Delete it, and it’s gone. In general, UNIX has no Undo function.
Terminal is a built-in tool for macOS, but not all Mac users are aware of its usefulness. It is a powerful command-line interface and can be used to do a lot of things on your Mac device without stress. With Terminal, all you have to do is simply input a command to get the desired output on your Mac.
Contents
- 2 Commands for Terminal
- 3 Final Verdict
Setting up Terminal Commands on Mac
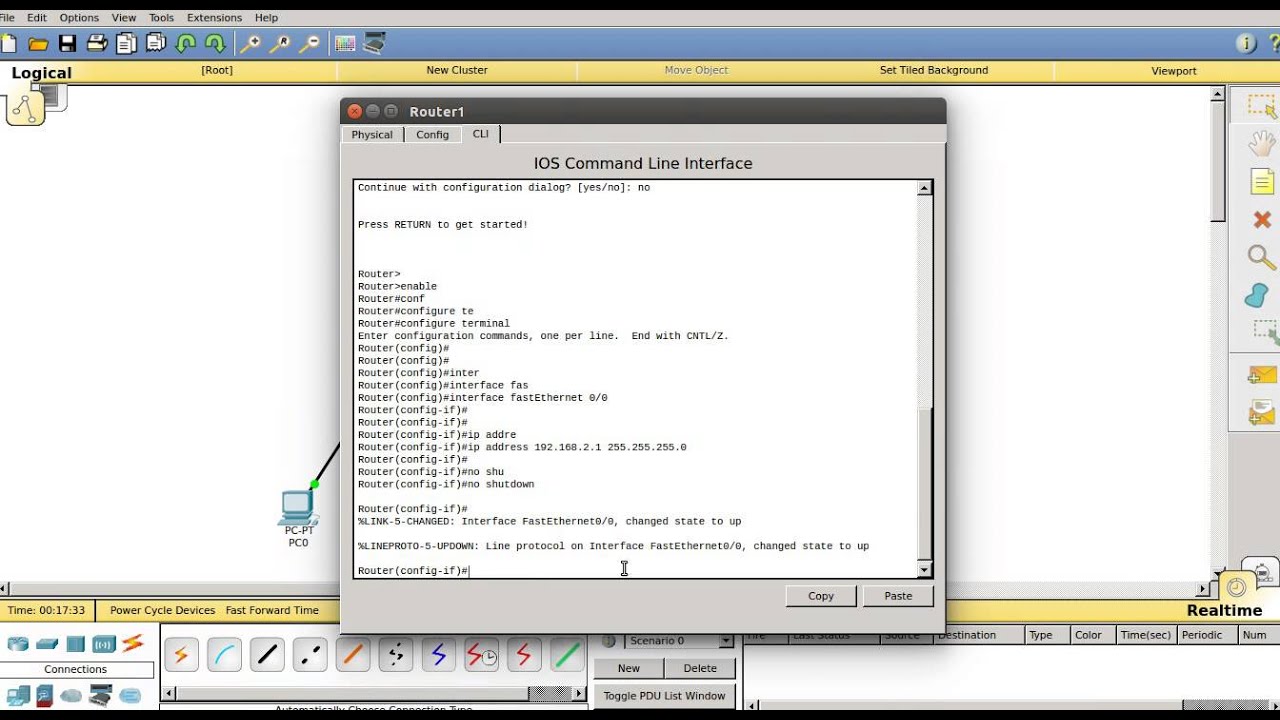
Before you can start using Terminal commands, you need to first locate the command prompt on your Mac device. Locate the prompt by taking the following steps:
- Open a Finder window or double click on the Macintosh HD icon.
- Find and open the Applications folder.
- After that, double click on Utilities.
- Here, you will find the Terminal. Click on Open the Terminal.
After doing this, it will take you to a window that shows the name of your PC, your username, and a dollar sign ($). All the terminal commands discussed below can be typed into the command prompt. Press the return key to go back to the command prompt.
Commands for Terminal
Mac users who do know about the built-in feature are occasionally hesitant to use Terminal. Any typo in your command could cause damage to your macOS. As long as you are careful and double-check your work, however, you should have no problem.
Here are some basic Terminal commands that you can use on your Mac device.
Check The Server Response
Ping is one of the most useful Terminal commands with which every Mac user should be familiar. This command will help you check the server response speed of domains and IP addresses. To perform this command, type into the command terminal ping [insert URL or IP address].
Keep Your Mac From Falling Asleep
Many Mac users do not know that there is a command you can use to keep your Mac awake or “caffeinated” for a certain amount of time before it goes into sleep or screensaver. To set this command type caffeinate –t 200000 into the command terminal. The command means that your Mac will stay awake for 200,000 seconds.
Show or Hide Files
Sometimes you might be looking for a file that is hidden on your Mac. You can use the following command to find their location on your system. To show all hidden files on your Mac device, type as follows: defaults Write com.apple.finder AppleShowAllFiles –bool TRUE. Directly underneath, type killall Finder.
This command will bring out all hidden files on your Mac and allow you to either edit or delete them. You can also decide to hide these files again by simply replacing the TRUE with FALSE.
Duplicate Files Between Folders on Your Mac
The can avoid the stress of copying and pasting files between folders on your Mac by merely using the duplicate files between folders command. This is achieved by using the Ditto terminal command on your Mac device. In the Terminal command prompt, type in Ditto [Original Folder] [New Folder].
Note: if you have folders in different locations with the same name, you have to include -v after Ditto to be able to achieve the right result.
Check For MacOS Updates
Your Mac device is customarily configured to check for macOS updates on a weekly basis, but a simple Terminal command can change this setting: defaults write com.apple.softwareUpdate ScheduleFrequency –int 1. Change the integer (the number seen in the command) to any number of your choice. The number represents the number of days that your device will wait before checking for updates.
You can return to the default weekly check for updates with defaults write com.apple.softwareUpdate ScheduleFrequency –int 7. With this, you can be notified of your app updates or macOS updates more frequently.
Improve Your Mac’s Screenshots
Normally, when you take screenshots on your Mac device, you will notice that it usually adds a drop shadow. These shadows can lower the quality of your screenshots. You might want to turn off these shadows by using the Terminal command defaults write com.apple.screencapture disable-shadow –bool TRUE. Underneath what you just typed, include Killall SystemUIServer. After entering this command, there should be no drop shadows added to your screenshots again.
Terminal Commands For Macbook
Final Verdict
Mac Terminal Tutorial
Many Mac users depend on various app preferences to have total control over their system. Terminal commands allow you to have total control without having to do this. You can use any of the terminal commands above, and many more, to customize your Mac device.
Terminal Commands For Mac Os X
Related Posts:
